Prescription compounding creates customized medications for patients by combining ingredients in specific dosages, forms, and strengths based on a prescription order. Furthermore, compounded medications are tailored to meet the unique needs of patients who may require specific medications not available in standard forms or strengths. Compounding can involve various medications, including creams, ointments, gels, solutions, suspensions, suppositories, and capsules. It can also include customized medications to be free of certain allergens, dyes, or other ingredients a patient may be sensitive to.
Compounding pharmacists work closely with physicians, dentists, veterinarians, and other healthcare providers to create medications specifically designed to meet the unique needs of their patients. Let’s explore different factors and compounding pharmacy benefits.
What Is Compounded and Non-Compounded Prescription?
A prescription can either be compounded or non-compounded. A compounded prescription is a prescription that requires a pharmacist to prepare a medication by combining individual ingredients in the pharmacy. Compounding pharmacy allows pharmacists to customize medications to meet the unique needs of individual patients, such as adjusting the strength, dosage, form, or flavor of a medication. Compounded medications are typically not commercially available and are made on a case-by-case basis. Thus, it would be best to consider common compounding formula types for better understanding.
In contrast, a non-compounded prescription is a prescription that specifies a commercially available medication that is already prepared and packaged by a pharmaceutical manufacturer. The pharmacist fills the prescription by dispensing the specified medication in the quantity and dosage form indicated.
How to Write a Compounding Prescription?

A compounding prescription is a prescription that requires a pharmacist to prepare a medication that is not commercially available.
Here is writing and filling an online prescription guide:
- Start with the patient’s name and basic information such as age and weight.
- Include the name and strength of the active ingredients that the medication will contain.
- This should be written in the generic form of the drug.
- Indicate the desired dosage form, such as a cream, ointment, solution, or capsule.
- Specify the quantity of the medication that the patient will need using both numeric and written formats.
- Include any necessary directions, such as how often the medication should be taken or applied.
- If the medication has special storage requirements, such as refrigeration, indicate this on the prescription.
- Sign and date the prescription, including your name and contact information.
It’s important to note that writing a compounding prescription requires special knowledge and training, and that’s why it should only be done by a licensed healthcare provider familiar with the specific compounding requirements and regulations.
What Are 4 Main Parts of a Compound Prescription?
A compound prescription typically consists of four main parts. Here is the pharmacy prescription process with basic parts to consider.
Superscription

This is the first part of the prescription and includes the symbol “Rx” (an abbreviation of the Latin word “recipe,” meaning “take”) followed by the name and address of the prescribing healthcare provider.
Inscription
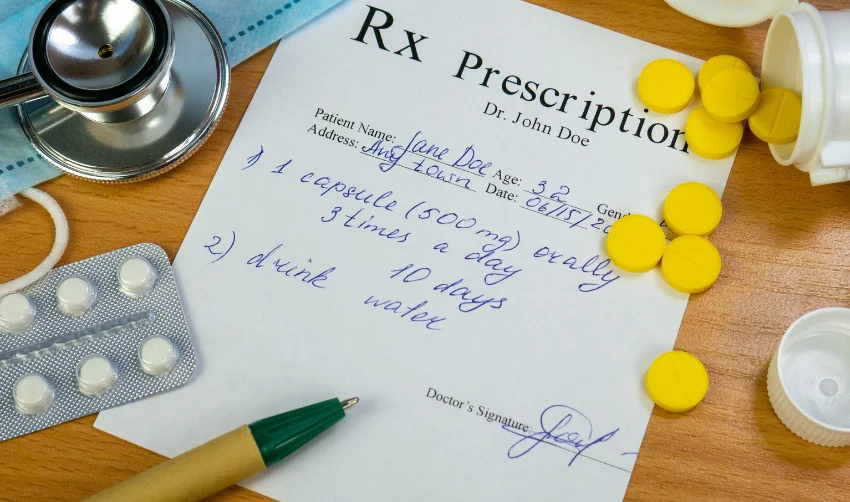
The inscription is the main body of the prescription and includes the names and amounts of the active ingredients and the medication’s strength and dosage form.
Subscription

This part of the prescription directs the pharmacist on preparing the medication, such as the type of vehicle or base to use and any required additives or flavorings.
Signature
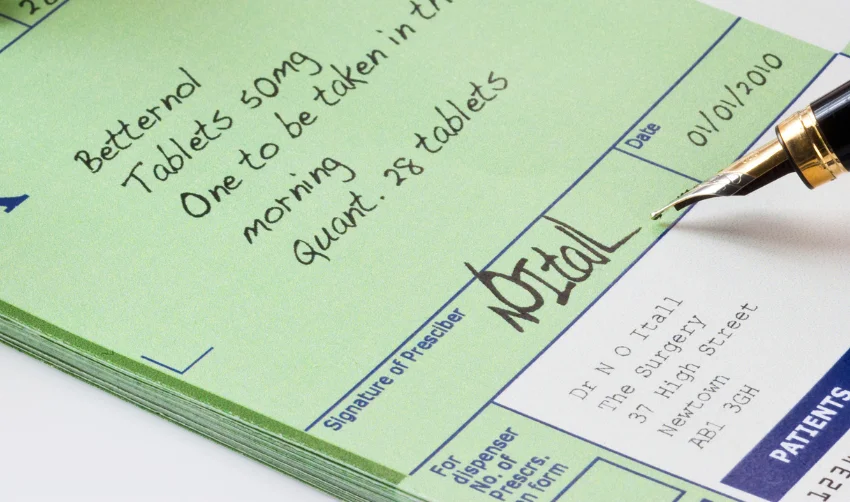
It is the final part of the prescription. It includes instructions for the patient on taking the medication and any other necessary information, such as warnings or precautions.
How Do You Calculate Compounding in Pharmacy?
Compounding in pharmacy refers to preparing customized medications for individual patients based on their needs. Compounding often involves mixing different medications or adjusting dosages to create a unique formulation tailored to the patient’s needs. When calculating compounding in pharmacy, it is important to consider compound guidelines such as principles of compounding mathematics, including ratios and proportions. Always consider the best online prescription refill in Maryland to get the best prescription.
The specific calculations involved in compounding will depend on the medication being prepared, the patient’s requirements, and the desired dosage form.
For example, suppose a patient needs a certain medication in a liquid form instead of a tablet. In that case, the pharmacist may need to calculate the appropriate volume of medication to add to the liquid base. Furthermore, when compounding medications that involve multiple active ingredients, pharmacists must consider the potential for drug interactions and adjust dosages accordingly.
Takeaways
While pharmacy compounding has been an essential part of pharmacy practice for many years, the field continues evolving with new technological advances, techniques, and ingredients. Today, compounding pharmacists play an important role in patient care, working closely with healthcare providers to provide personalized treatment options that meet each patient’s unique needs.
Overall, compounding in pharmacy requires careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of pharmacology, mathematics, and the principles of dosage calculation. Pharmacists must work closely with physicians and other healthcare professionals to ensure that the compounded medication is safe and effective for the individual patient.


